Time to revisit some statistics that put the gender wage gap into perspective. According to the August 2012 Women’s Earnings and Income report from Catalyst, the following statistics are accurate:
- The median annual earnings for full-time, year-round women workers in 2010 was $36,931 compared to men’s $47,715.
- In 2011, the median weekly earnings for full-time working women was $684, compared to $832 for men.
- In 2011, the median weekly earnings for women in full-time management, professional, and related occupations was $941, compared to $1,269 for men.
- In 2009, of the 32,280,000 dual-career couples, wives earned more than their husbands 28.9% of the time, up from 17.8% of the 29,755,000 dual-career couples in 1987.
- In 2010, full-time working married women with spouses present had median usual weekly earnings of $727, somewhat higher than never married women ($591) or women of other marital status (divorced, separated, or widowed – $653).
- In 2010, married men with spouses present had median usual weekly earnings of $939, significantly higher than never married men ($608) or men of other marital status ($774).
- In 2011, Asian women who were full-time wage and salary workers had higher median weekly earnings than women of all other races/ethnicities as well as African-American and Latino men.
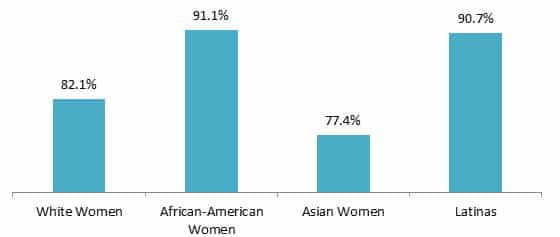
The gender gap exists within multiple races/ethnicities as shown in the chart below.
Women’s Earnings as a Percentage of Men’s by Race/Ethnicity
The wage gap in the United States is significant as the following statistics show:
- Based on median annual earnings for full-time, year-round workers, women earned 77.4% of men’s earnings in 2010.
- Based on the median weekly earnings for full-time workers, (which excludes self-employed and full-time workers who work only part of the year), in 2011 women earned 82.2% as much as men. In 1979, women earned 62.3% as much as men.
- The earnings difference between women and men varies with age, with younger women more closely approaching pay equity than older women (2010, median weekly earnings), for full-time wage and salary workers.
- The gender wage gap also varies by industry. The biggest wage gap in the U.S. is in the Financial Activities industry, with women earning 70.5 cents for every dollar men make.
You can find more details and statistics, including data from countries around the world, on the Catalyst website. Links to sources are also available in the Catalyst report.
Image: Catalyst




